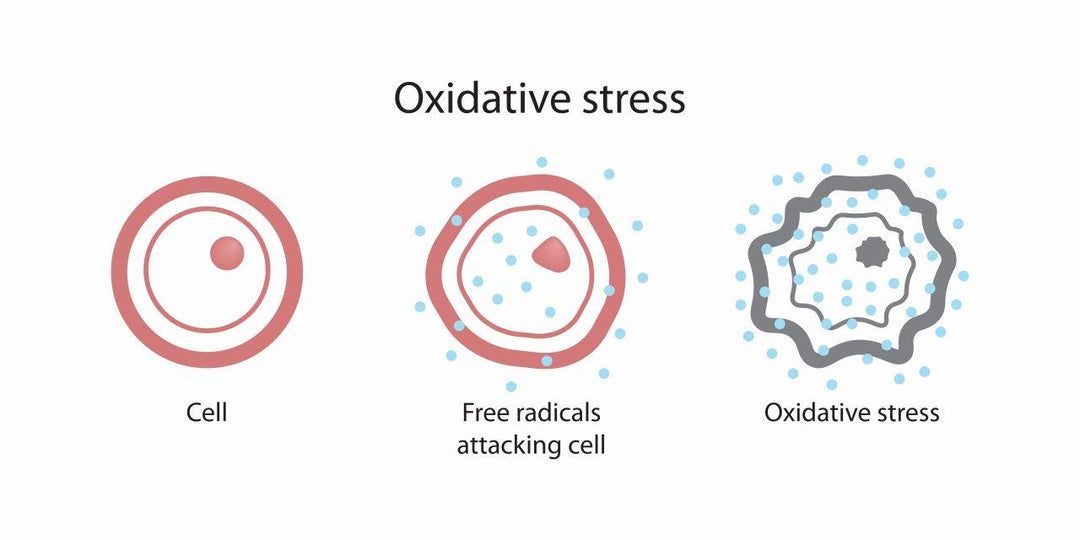
Oxidative stress results from an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body's antioxidant defense mechanisms. Free radicals, a subset of ROS, are highly reactive molecules with unpaired electrons that can initiate a chain reaction of oxidative damage within cells. Over time, prolonged exposure to free radicals, induced by environmental factors, metabolic processes and unhealthy lifestyle choices like stress, processed food, alcohol and nicotine, can lead to cellular deterioration. The detrimental effects of oxidative stress and free radicals on cellular components, such as proteins, lipids, and DNA, are closely linked to accelerated ageing and increased vulnerability to age-related diseases.
Antioxidants play a vital role in combating oxidative stress by neutralizing harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS) within the body. Antioxidants, such as Astaxanthin, Fisetin or Lutein, work to donate electrons to free radicals, preventing them from causing oxidative damage to cellular structures. By bolstering the body's natural defense mechanisms, antioxidant supplementation helps to mitigate the negative effects of oxidative stress and to contribute to overall cellular health.
Oxidative Stress
Over time, prolonged exposure to
oxidative stress, induced by environmental factors, metabolic processes and unhealthy lifestyle choices like stress, processed food, alcohol and nicotine, can lead to cellular deterioration.