THE NMN BREAKTHROUGH BACKED BY HARVARD UNIVERSITY SCIENCE
The Most Advanced Cellular Energy & Anti-Ageing Supplement
Your Body’s Battery is Running Low—Recharge It Now
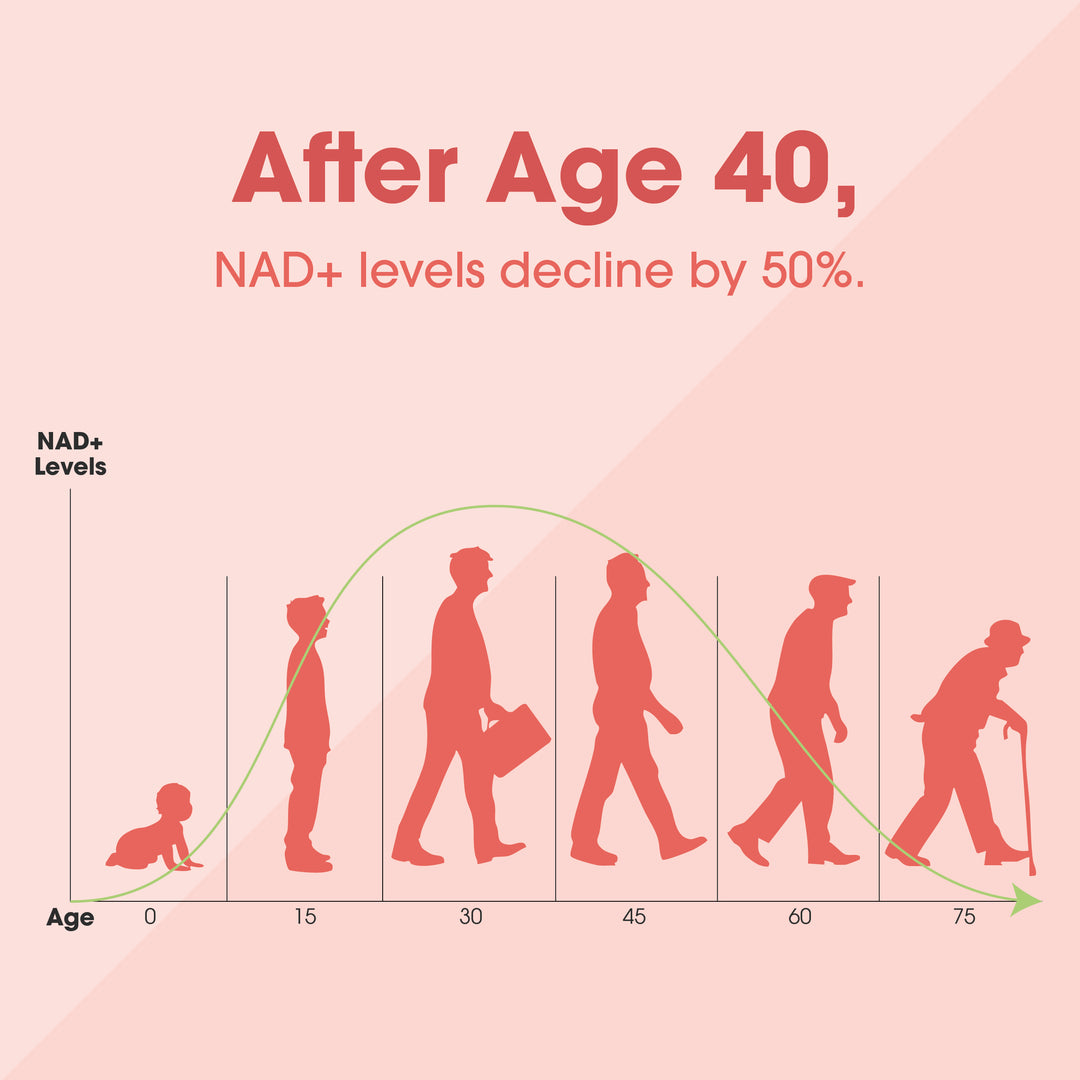
By the time you turn 40, your NAD+ levels drop by 50%—leading to fatigue, slower recovery, and accelerated ageing. But what if you could restore your body's natural energy and vitality?
The Science is Clear: NAD+ is the Key to Longevity
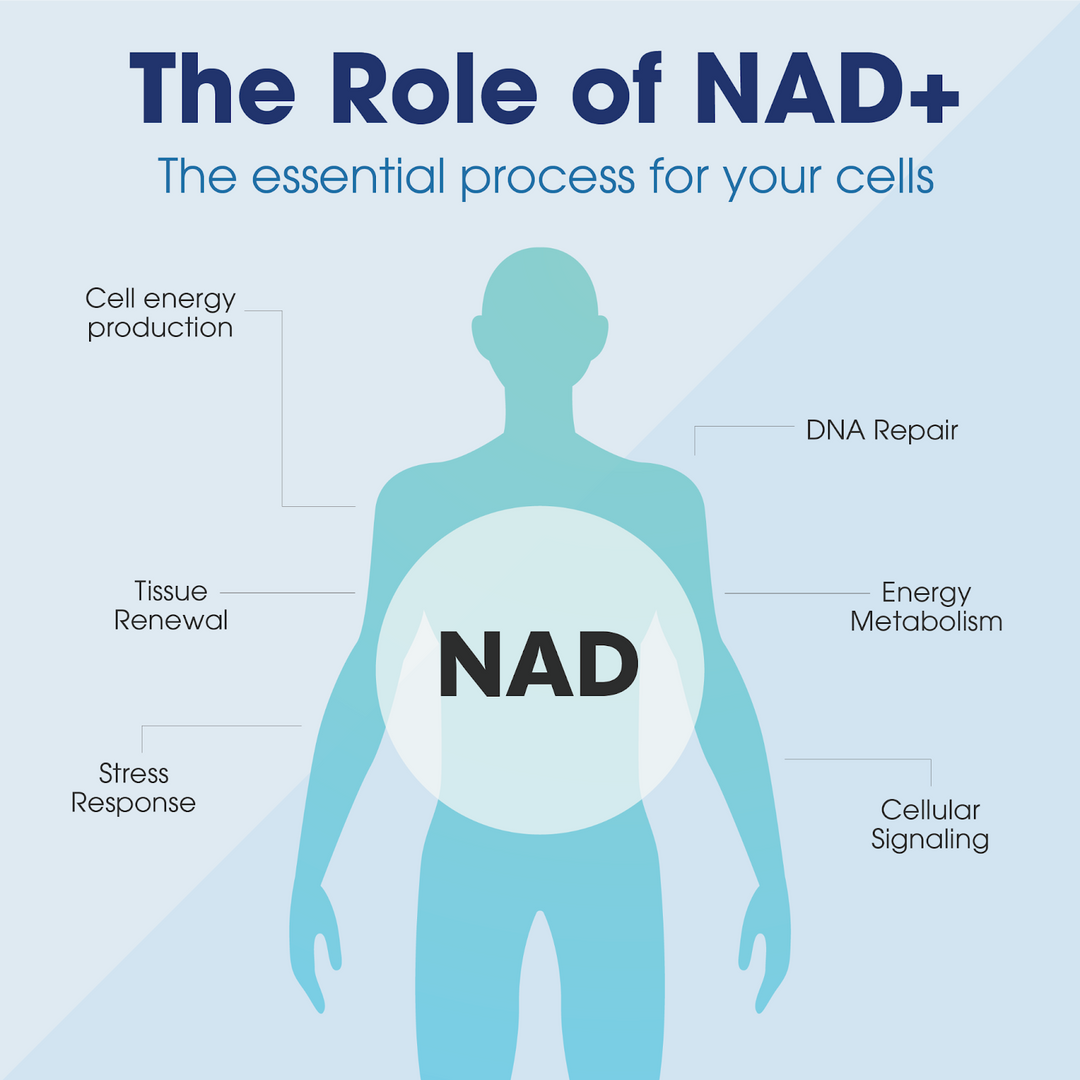
NAD+ is the powerhouse coenzyme that fuels every cell in your body. It supports energy production, DNA repair, and healthy ageing. However, NAD+ levels decline over time, leaving you feeling sluggish and worn out.
NMN: The Cellular Fuel for Longevity
NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) is a direct precursor to NAD+, proven in studies by Harvard University and other leading
institutions to restore cellular function, boost metabolism, and support longevity.
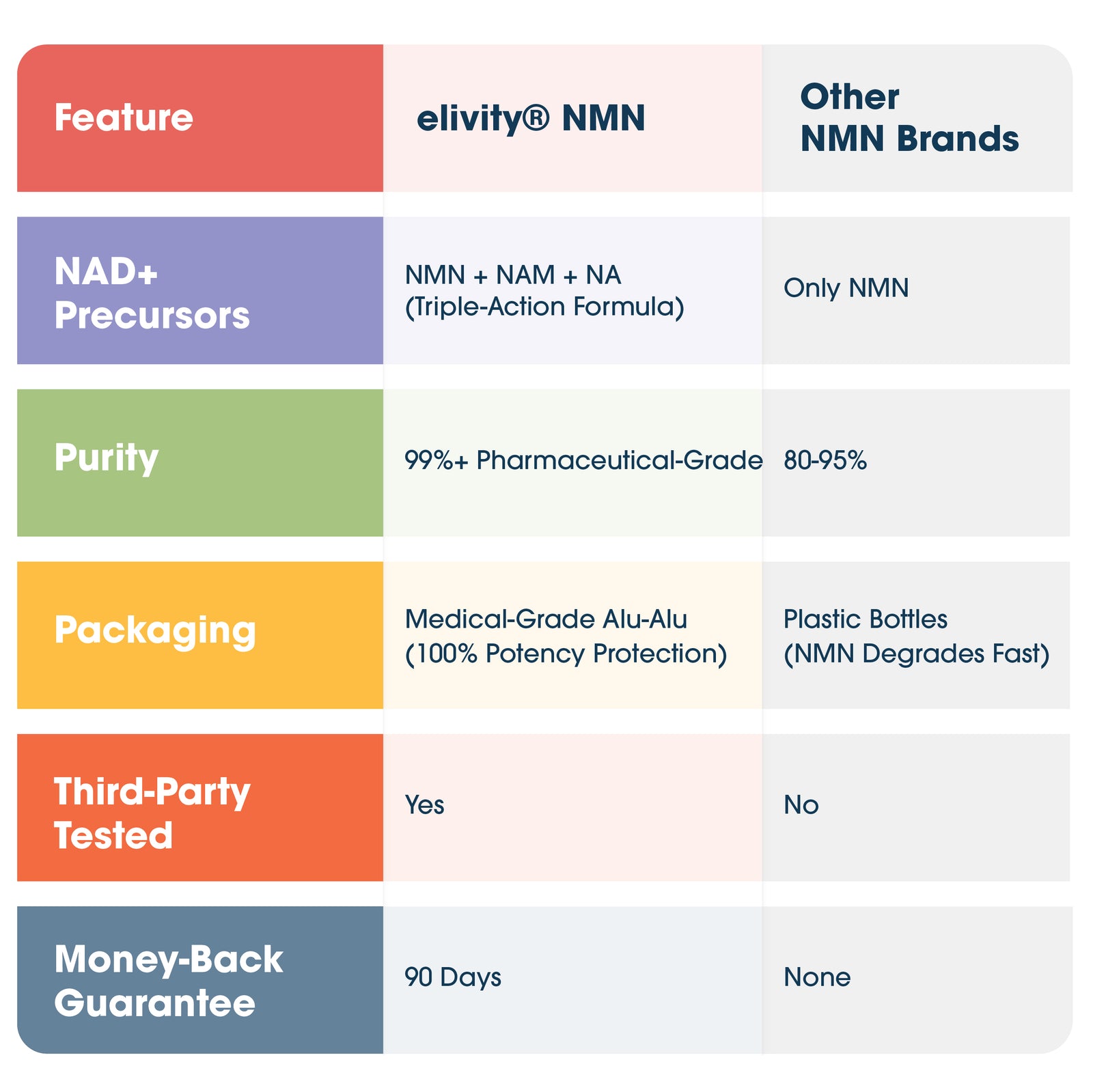
Why elivity® NMN is the Gold Standard
Not all NMN supplements are created equal. Here’s why elivity® cell energy stands above the rest:
✅ Triple-Action Formula for Maximum Absorption – Unlike standard NMN supplements, our formula includes Nicotinamide (NAM) and Nicotinic Acid (NA) for superior NAD+ production and
effectiveness.
✅ Clinically Proven Potency – With over 99% purity, our NMN is scientifically formulated for maximum impact.
✅ Medical-Grade Alu-Alu Packaging – Protects NMN from air, moisture and UV radiation ensuring 100% potency in every dose. Most NMN supplements degrade before they even reach your body—ours doesn’t.
✅ Results
You Can Feel in Just Weeks – Experience increased energy,
sharper focus, and improved recovery in as little as 2-4 weeks.

The elivity® Standard: Science, Purity, and Performance
✔ Made in Australia
✔ Third-Party Tested for Purity & Safety
✔ Halal & Vegan Certified
✔ 90-Day Money-Back Guarantee
Don’t Let Ageing Slow You Down—Stay at Peak Performance.
Replenish your body’s energy at the cellular level and feel the difference.
👉 Try elivity® NMN Today—Backed by Science, Engineered for Results.
Discover the benefits of cell energy capsules, ideal for individuals seeking a significant energy boost while aiming to maintain youthful vitality. If you're experiencing increased fatigue, prolonged recovery times after physical activities, or a sense of slowing metabolism leading to weight gain, consider integrating cell energy into your daily routine. With just a click, unlock the potential for a life full of vitality.
NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) 440mg
NMN is a naturally occurring molecule essential for the body's synthesis of NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide). This coenzyme is pivotal for mitochondrial function, the cellular powerhouses responsible for converting food and oxygen into energy. Insufficient NAD+ levels may result in cellular energy depletion.
Nicotinic Acid (Niacin) 7mg
Nicotinic Acid, commonly known as Niacin, supports cardiovascular health. Additionally, Niacin aids in energy metabolism, facilitating the conversion of food into energy, and contributes to the maintenance of healthy skin, nerves, and digestive function.
Nicotinamide 7mg
Nicotinamide, a form of vitamin B3, inhibits key longevity-promoting proteins called Sirtuins within cells. Sirtuins are crucial NAD+-dependent enzymes involved in cellular metabolism and repair processes. Nicotinamide can undergo a two-step conversion process via the salvage pathway to generate NAD+. NAD+ is indispensable for energy metabolism, particularly crucial for mitochondrial function, the cellular sites responsible for energy production from food and oxygen.
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+)
NAD+ is a crucial coenzyme present in all our cells, essential for metabolizing nutrients from food. Its interaction with proteins offers various benefits, including DNA and cell repair. NAD+ is particularly vital for the functioning of mitochondria, the cellular powerhouses responsible for converting food and oxygen into energy. In simple terms, NAD+ undergoes a process where it accepts an electron from one molecule to become NADH. Subsequently, NADH donates the electron to another molecule, reverting back to NAD+, facilitating enzymatic activity crucial for maintaining bodily health.
NAD+ and Clinical Studies
Although the body can produce NAD+, human clinical studies indicate a decline in this ability with age. By age 50, NAD levels are typically half of what they were at age 20, with this decline beginning as early as our 30s. NAD+ can be synthesized from the amino acid tryptophan or via salvage pathways, requiring a preformed pyridine ring.
Synthesis from Nicotinamide and Nicotinamide
Synthesis from Nicotinamide and Nicotinamide Riboside involves a two-step process, where Nicotinamide is converted to NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) by phosphoribosyl transferase. Synthesis from Nicotinic Acid follows a three-step process through the Preiss-Handler pathway. Initially, it is converted into Nicotinic Acid Mononucleotide, then further into Nicotinic Acid Adenine Dinucleotide, utilizing both Nicotinamide and Nicotinic Acid substrates. NAD+ is ultimately produced in a reaction catalyzed by NAD synthetase.
FAQs
✔️ Do you feel your energy levels need a boost?
✔️ Do you get tired and exhausted more easily than a few years back?
✔️ Does it take you longer to recover from workouts and sport activities?
✔️ Do you feel your metabolism is slowing down and you put on weight more easily?
By the time we reach 50 years, our NAD levels are only half the levels we had when we were 20 years old — and the decline starts as early as our 30s. That’s why first signs and symptoms of ageing can start already in our 30ies, depending on our lifestyle and diet.
We highly recommend to pursue a pro-active health approach and keeping your cells and body healthy at the first place and not to wait and cure problems instead. At elivity we believe that healthy ageing is not an elusive concept but an achievable reality within everyone's grasp.
cell energy is suitable for people in their 30ies, even if they don’t yet feel a significant decline in their energy levels. Its core ingredient NMN is one of the most popular and well-studied longevity substances and has the ability to positively impact 7 hallmarks of aging at the same time.
cell energy is certainly a “must- have” product, if you aim to keep your energy levels and metabolism at a youthful level!
NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) is a naturally occurring molecule which is a precursor of NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide).
NMN is a driving force in the body’s production of NAD+, which is an essential coenzyme involved in multiple biological processes, including ageing and gene expression. NMN has its very own transporter, Slc12a8, which shuttles the NMN molecule directly into the cells where it’s used for NAD production.
NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is a coenzyme found in all of our cells. It is essential for the metabolic processing of nutrients from our food and binds with proteins to help a variety of benefits such as DNA repair and cell repair. So it plays a vital role in energy metabolism and maintaining proper cell functioning.
Besides NMN cell energy’s formula contains Nicotinic Acid, commonly known as Niacin, and Nicotinamide. Both active
ingredients can be converted into NAD+ in our bodies - through various, different pathways and aim to keep your energy levels and metabolism at a youthful level.
Ideally, cell energy becomes your long-term companion on your path to youthful and healthy ageing. It’s like integrating a healthy diet or exercise habit: doing a little for a short period will benefit your health, but making it a consistent habit will reward you with optimal results. That way cell energy can continuously provide your cells with sufficient energy. It will help to slow down the ageing process and reward you with an optimized health- and lifespan.
Please check our subscription model with great savings to start your youthful ageing journey now!
Yes, absolutely! In fact, our products are formulated to complement each other, and the best results are achieved if they are taken in combination. Every elivity product is formulated to address a different category within the broad spectrum of longevity mechanisms and cell health. To optimize your healthy ageing process, check out our elivity longevity bundles .
As with any health supplement or nutraceutical we strongly advise you to consult with your health practitioner before taking elivity cell energy capsules.
Yes, our cell rejuvenation capsules are suitable for vegetarians as well as vegans. We don’t use any animal derived ingredients and we use HPMC (Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose) capsules.
Yes, cell energy is gluten free and suitable for people who suffer from coeliac disease.
elivity cell energy is Halal certified by the Australian Halal Authority & Advisers. The product is produced according to Islamic rites and is halal. It can be consumed by Muslims in any part of the world.
Consume 1 capsule each day with a beverage at a time that suits you best, whether it be in the morning or at lunch. cell energy can be taken with food, or it's fine to take it on an empty stomach as well.
cell energy should be stored in a dry place, away from heat and light.
elivity’s Alu-Alu blister packaging offers the best solution for supplement protection, shielding our formulations from external factors such as light, moisture, and air, ensuring the stability and efficacy of the product over time. Additionally, the tamper-evident and barrier properties of Alu-Alu blisters enhance product safety and integrity, assuring our costumers of the quality and freshness of our capsule products.
It is important to follow our recommended dosage and directions for use. elivity products are safe and should not cause any undesirable side effects. However, if you are taking prescription medicine or if you are dealing with a certain health and medical condition, we advise to consult with your doctor first before adding our products to your supplement routine.
Every ingredient and its dosage is backed by scientific studies, every formulation is science and evidence based. elivity cell energy capsules are developed and manufactured in Australia, in a TGA (Therapeutic Goods Administration) approved facility. Australia is known for its industry-leading strict complementary medicine and health supplement standards including regulatory matters, ingredients and their purity, as well as manufacturing standards. With elivity supplements you are choosing not only the best quality within the longevity industry but also a brand that values trust, credibility, reliability and responsibility for customers.
At elivity we pride ourselves in working and collaborating with highly reputable and industry-leading scientists and experts. We aim for the highest quality standards in everything we do – starting from the formulation process all the way to manufacturing and shipping.





















